One ear hearing problem, which is medically known as unilateral hearing loss, is a condition where a person loses the ability to hear in one of the ears, while there is normal functioning in the other. This can occur suddenly or gradually. A decrease in the audibility of one ear can cause hindrance in daily activities, such as the inability to hear phone calls or people. It is important to get your ears tested at the first sign of it.
What is unilateral hearing loss?
Unilateral hearing loss is a sudden or gradual loss of hearing in only one ear. A hearing problem in one ear may occur due to a variety of reasons. The levels of hearing can range from mild to severe. The symptoms can range from muffled hearing to complete hearing loss in one ear. Timely treatment by a professional ensures that the symptoms do not progress further.
What are the types of hearing loss on one side?
Hearing problem in one ear can be of various types depending on which part of the ear is affected, and its degree. It can be divided into 3 categories:
Conductive Hearing Loss (One Ear)
This occurs when the sound is unable to pass through the outer or the middle area of the ear due to the excess accumulation of earwax, fluid or ear infections. This often causes muffled hearing and is usually temporary, and can be treated via medications or minor surgery.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss (One Ear)
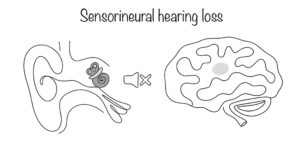
Sensorineural hearing loss in one ear is caused when there is damage to the auditory nerves or the cochlea due to ageing, head injury or other reasons. It can be sudden and severe, which leads to permanent hearing loss in one ear. Assistance of auditory devices like hearing aids is required in this case to improve hearing ability.
Mixed Hearing Loss (One Ear)
As the name suggests, it is a combination of the above two, that is, blockage or damage of the middle or outer component of the ear, along with damage to the inner ear. The conductive component is treated first, followed by the sensorineural component.
It is important to avoid self-treatment in such cases, as proper diagnosis by a specialist is required to avoid worsening of the symptoms.
What are the signs and symptoms of one-sided hearing problems?
It is important to be cautious of hearing loss symptoms to ensure their timely treatment. The symptoms are as follows:
Common symptoms
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves
- Turning the head to hear clearly
- Muffled or unclear sounds
- Turning up the volume on TV, radio, or phone
- Trouble hearing high-pitched sounds like doorbells or alarms
Associated symptoms
- Ringing, buzzing, or humming in the ears (tinnitus)
- Ear pain or pressure
- Dizziness or balance problems
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Sensitivity to certain sounds
What causes hearing loss on one side?
Hearing loss in one ear can be caused by many factors, ranging from ear blockage to internal auditory damage. These causes can be grouped into common, sudden and medical.
Common causes
- Earwax buildup: Excess accumulation of earwax in the ear canal is one of the leading causes
- Ear infections: Entry of external material, such as bugs, bacteria, or respiratory infections, can infect the ear canal and eardrum
- Fluid in the middle ear: When the tube connecting the ear to the respiratory system gets blocked or swollen, it can accumulate fluid in the middle ear due to a lack of airflow or allergies.
- Exposure to loud noise: Exposure to noise over a certain decibel level can damage auditory nerves or the cochlea.
- Age-related hearing changes: As people age, the auditory nerves get weaker, which reduces hearing ability.
- Eardrum damage: loud noise, physical pressure and many other factors can damage the eardrum.
Sudden causes
- Head injury or trauma: Severe head injuries can disrupt auditory parts, causing hearing loss.
- Sudden changes in air pressure (barotrauma): Imbalance of airflow due to altitude changes can affect hearing ability.
- Viral infections: Respiratory infections like cold or flu can infect the inner ear.
- Acoustic shock: Sudden loud noises like explosions or gunshots can cause immediate damage to the inner ear.
Medical causes
- Meniere’s disease: Chronic ear disorder caused by fluid buildup in the inner ear.
- Acoustic neuroma (benign tumour on the hearing nerve): A tumour that grows gradually on the main ear nerve
- Otosclerosis: bone in the middle ear remodels unusually, which reduces its ability to vibrate, causing hearing loss.
- Autoimmune inner ear disease: It is a condition where the immune system attacks your own inner ear cells, causing rapid ear loss.
- Diabetes or circulatory problems: High blood sugar gradually damages cochlea’s vessels.
- Neurological disorders: Causes hearing loss mainly through sensorineural hearing loss by damaging the auditory nerves.
Also Read: Causes of Sudden Hearing Loss and Why You Should Not Ignore Them?
How is unilateral hearing loss diagnosed?
Many causes lead to hearing loss in one ear. A diagnosis by a professional is recommended to determine the root cause to ensure proper treatment. The diagnosis process includes a series of steps that may vary according to test results.
- Firstly, the patient undergoes a medical history check and a physical examination of the ear by a trusted doctor.
- It is then preceded by a pure-tone audiometry test, where the patient is made to hear different levels of sound to measure hearing ability.
- This is followed by a speech test to check the extent to which a person can understand spoken words.
- Lastly, tympanometry is done to evaluate the functioning of the eardrum and the middle ear.
A few cases may require an MRI scan to rule out medical causes.
What are the treatment options for unilateral hearing loss?
Treatment options differ as per the cause and diagnosis. The treatment options are as follows:
- Earwax removal: In the context of conductive or mixed hearing loss due to earwax blockage, Professional methods are used to clean out the buildup in the ear canal.
- Infection treatment: Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, nasal sprays and other medications as prescribed by a specialist.
- Steroid therapy: In cases that are sudden or severe, steroids are used to reduce swelling/inflammation and speed up the recovery process.
- Hearing aids: Help increase the hearing ability, usually in the case of permanent damage.
- CROS/BiCROS systems: Non-surgical devices that transmit sounds from the poorly functioning ear to the better hearing ear.
- Auditory Therapy: Helps improve hearing and speech ability.
When to see a hearing expert?
The best time to visit a doctor is when you notice even the slightest possible symptoms of hearing loss in one ear. A professional diagnosis at an early stage can make the available treatment options effective. Delaying treatment only worsens the condition, thereby increasing its permanence. Symptoms that may require immediate attention are:
- Sudden hearing loss: Seek immediate care if hearing drops quickly in one ear.
- Dizziness or balance issues: May indicate inner ear problems that need urgent attention.
- Ear pain or discharge: Could signal an infection or injury.
- Persistent ringing in one ear: Ongoing tinnitus should be evaluated.
- Gradually worsening hearing: Recurring or increasing difficulty should not be ignored.
For queries or medical consultation, feel free to contact Dr Jay Jindal using the contact details provided.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. How do I take care of myself with unilateral hearing loss?
Unilateral hearing loss can cause discomfort and pain, depending on the symptoms. It is important to avoid self-treatment, have enough rest, avoid areas of loud noise and seek medical care as soon as possible.
Q.2. Is one-sided hearing loss permanent?
It may or may not be permanent, depending on the cause and diagnosis. Hearing loss in one ear caused by earwax blockage and ear infections are temporary and treatable, whereas head injuries and ear disorders may be permanent.
Q.3. Is unilateral hearing loss curable?
Unilateral hearing loss can be cured based on the category it falls into. Conductive hearing loss is temporary and can be cured easily, whereas sensorineural and mixed hearing loss can be more or less permanent.
Q.4. Can unilateral hearing loss be prevented?
Unilateral hearing loss may occur due to circumstances out of our control. Early diagnosis and treatment, avoiding areas of loud noise and following proper care can prevent unilateral hearing loss.
Q.5. How to fix deafness in one ear?
Firstly, it is important to visit a professional to find the right cause and treatment. Using medications and following proper care as prescribed by the doctor can help fix deafness in one ear.
Q.6. Why do I suddenly lose hearing in one ear?
Hearing loss in one ear can happen due to varying causes, and it’s degrees. Some of the common causes include earwax blockage, ear infections, and exposure to loud noise. For a proper diagnosis, it is important to consult a professional.